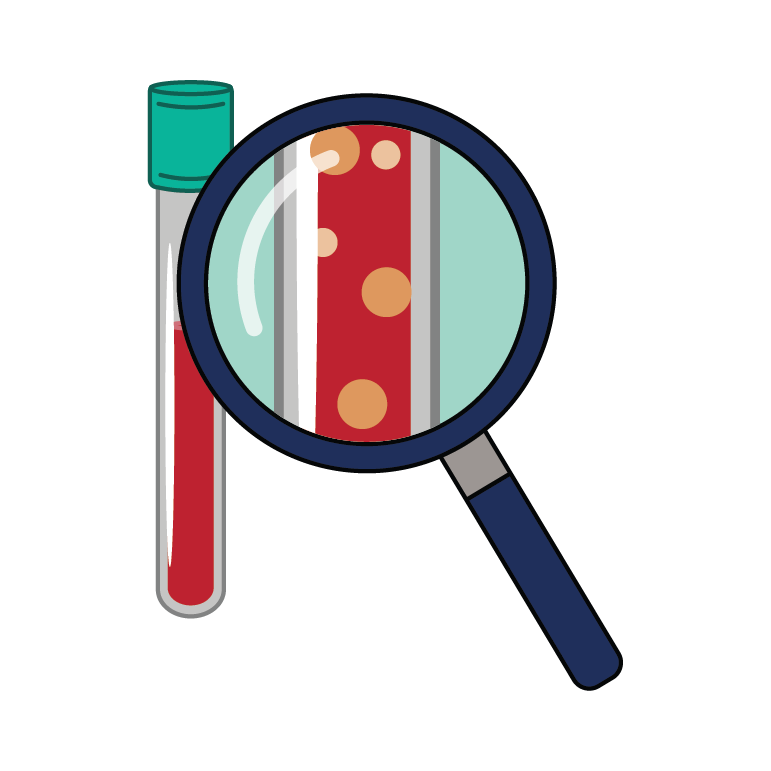
Hepatotoxicity
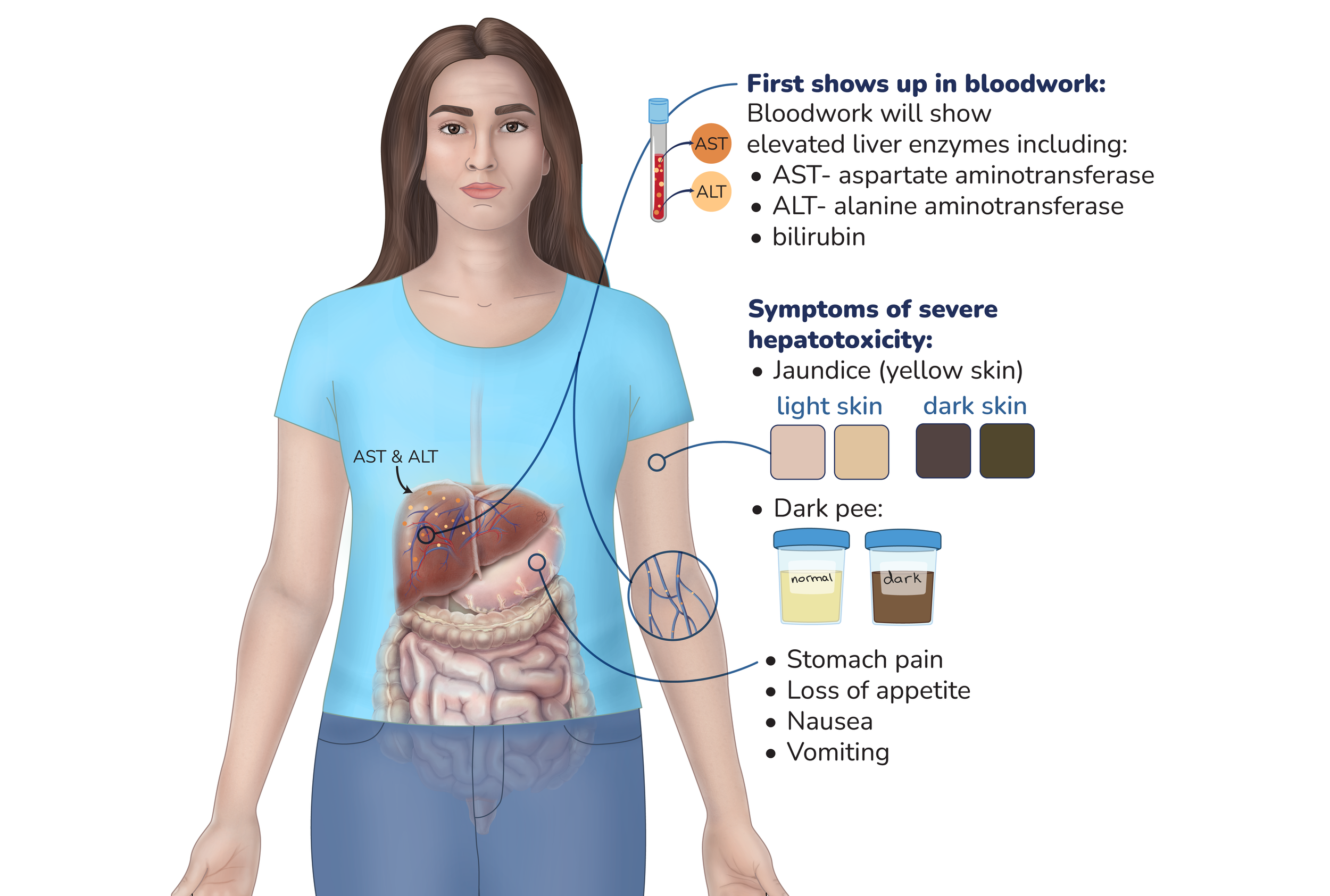
irritation or injury of the liver
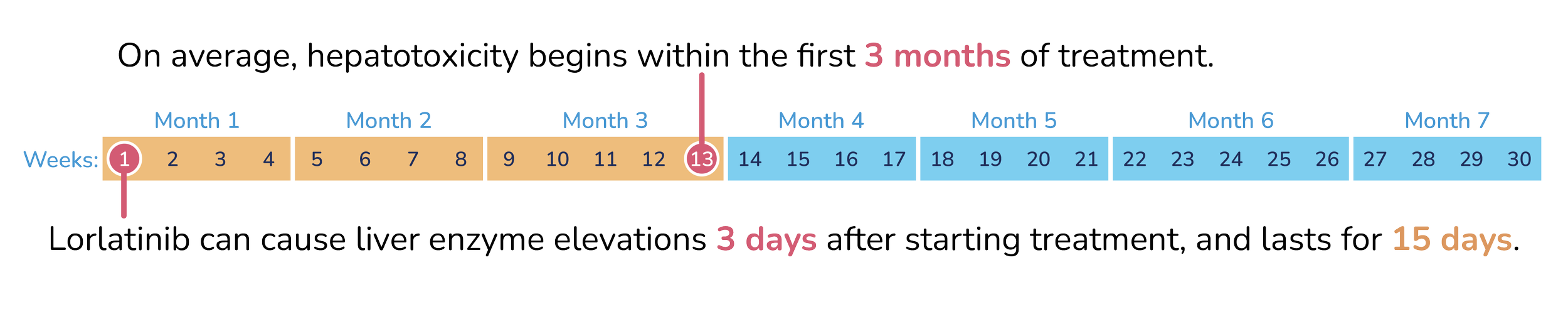
When does hepatotoxicity start and how long does it last?
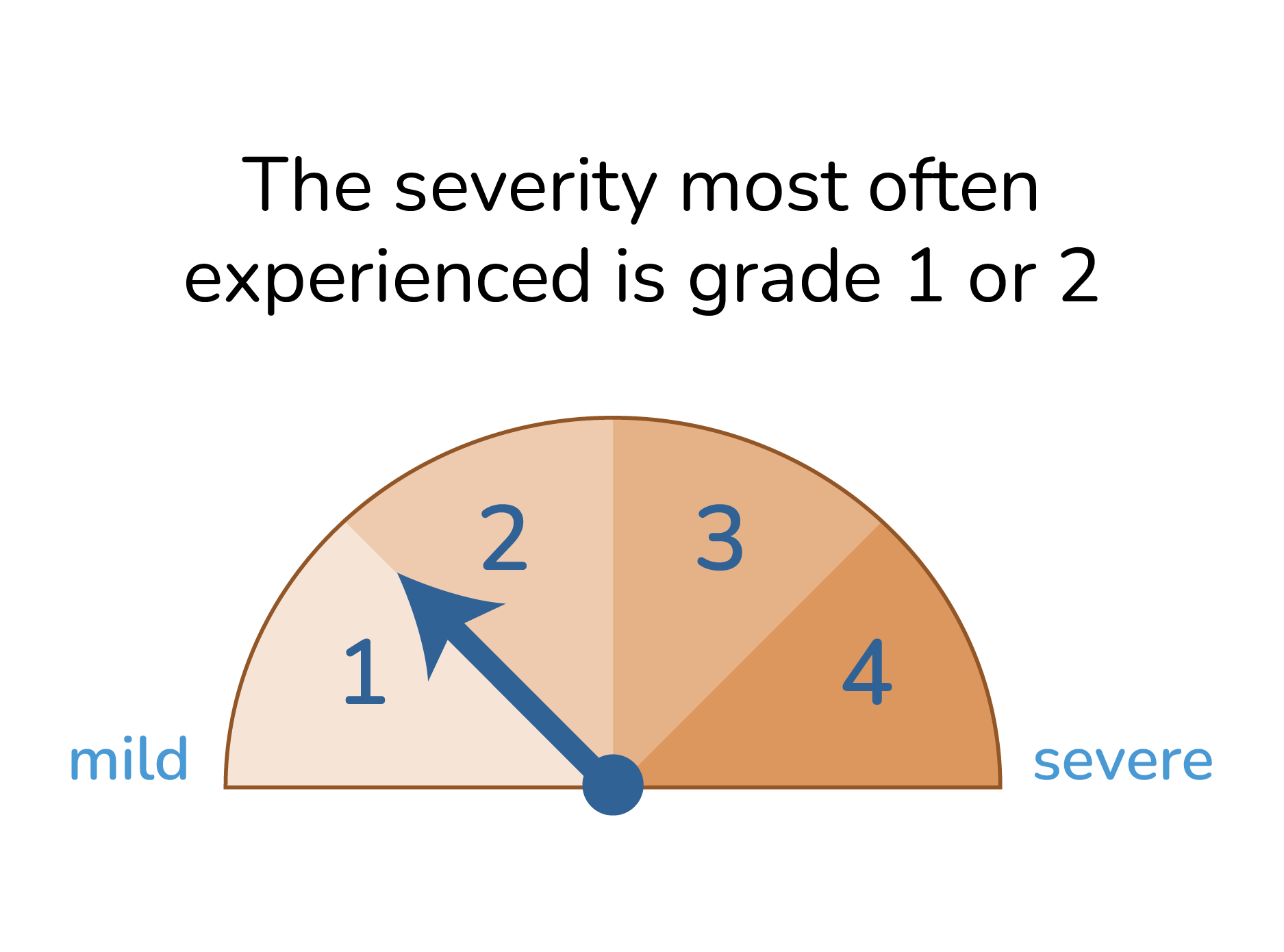
How serious is hepatotoxicity?
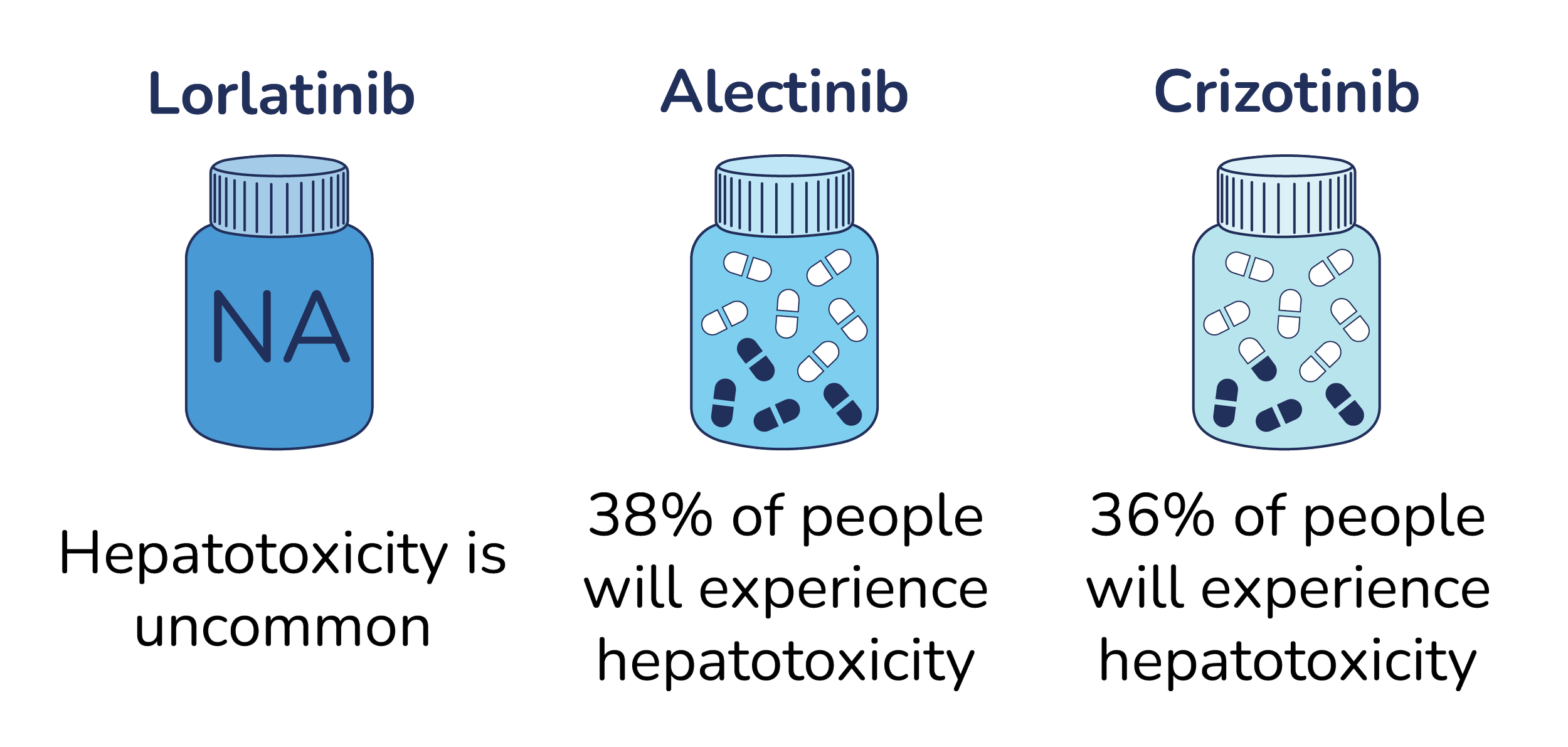
How likely is it that I will experience hepatotoxicity?
Prevention Strategies
-
Tell your healthcare team if you have a history of liver problems.
Liver function tests are monitored through bloodwork. These tests should be taken at the start of treatment and every 2 weeks during the first 2-3 months of treatment.
Why: this helps catch changes in liver function early and treat them before they become a problem.
-
Don’t smoke or drink alcohol.
Eat healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Why: Alcohol and the chemicals found in cigarettes (such as nicotine and tar) are toxic to the liver. ALKi themselves can cause liver damage so the liver is already under stress.
-
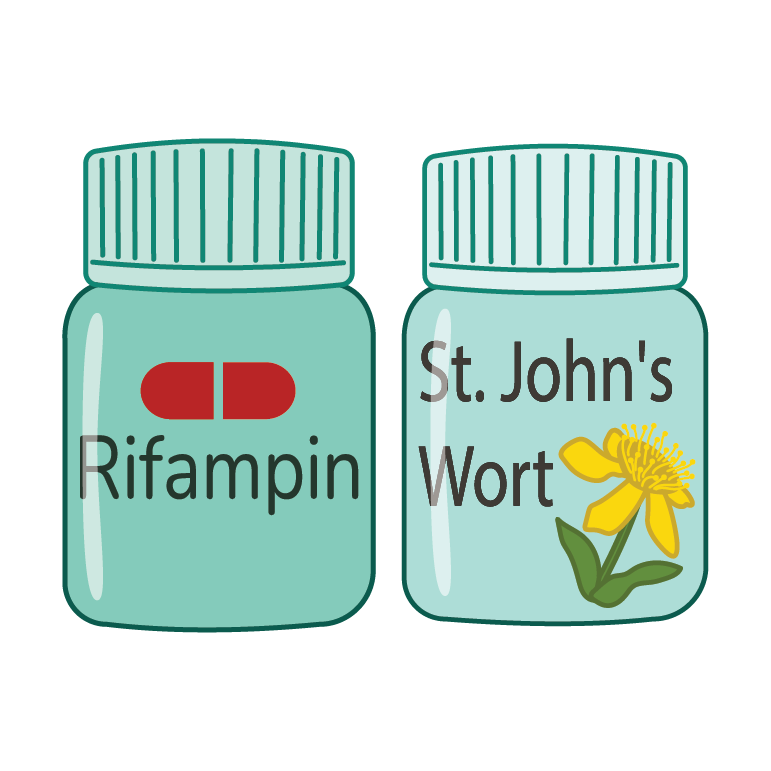
Talk to your doctor about medications, supplements, and herbal products that you use:
Rifampin is an antibiotic mainly used to treat tuberculosis or meningitis.
St. John's wort is a herbal product that can be found in oral supplements, teas, or creams, and is used to treat depression and symptoms of menopause.
Why: these products affect ALKi medications and can increase the risk of liver injury.
Management Strategies
-
Based on the grade (or severity) of hepatotoxicity your doctor will make adjustments to your medication.
Mild to moderate impairments require no adjustment. Your healthcare team will continue monitoring bloodwork.
-
Based on the grade (or severity) of hepatotoxicity your doctor will make adjustments to your medication.
Significant impairments require a temporary pause of medication until liver function returns to normal.
If liver function does not improve, your healthcare team might reduce the dose of ALKi.
-
Based on the grade (or severity) of hepatotoxicity your doctor will make adjustments to your medication.
Severe impairments require greater dose reductions or to permanently discontinue ALKi treatment.
Your healthcare team will likely recommend another type of ALKi or alternative treatment.
Emergent Symptoms
If you are unsure, it is always safer to seek medical care.
Tell emergency staff you are on an ALK inhibitor for lung cancer.
Call a Healthcare Provider
Call 811 for general health advice from a registered nurse OR call your care team
Not feeling hungry
Feeling sick to your stomach
Throwing up
Mild belly pain
Feeling more tired than usual
Itching with no rash
Light-colored poop
Visit an Emergency Room
Call 911 or drive to your closest emergency room
Yellow skin or yellow eyes
Dark brown urine
Strong pain on the right side of your belly
New confusion or very hard to stay awake
Throwing up that will not stop
Easy bruising or bleeding
Severe weakness or you collapse