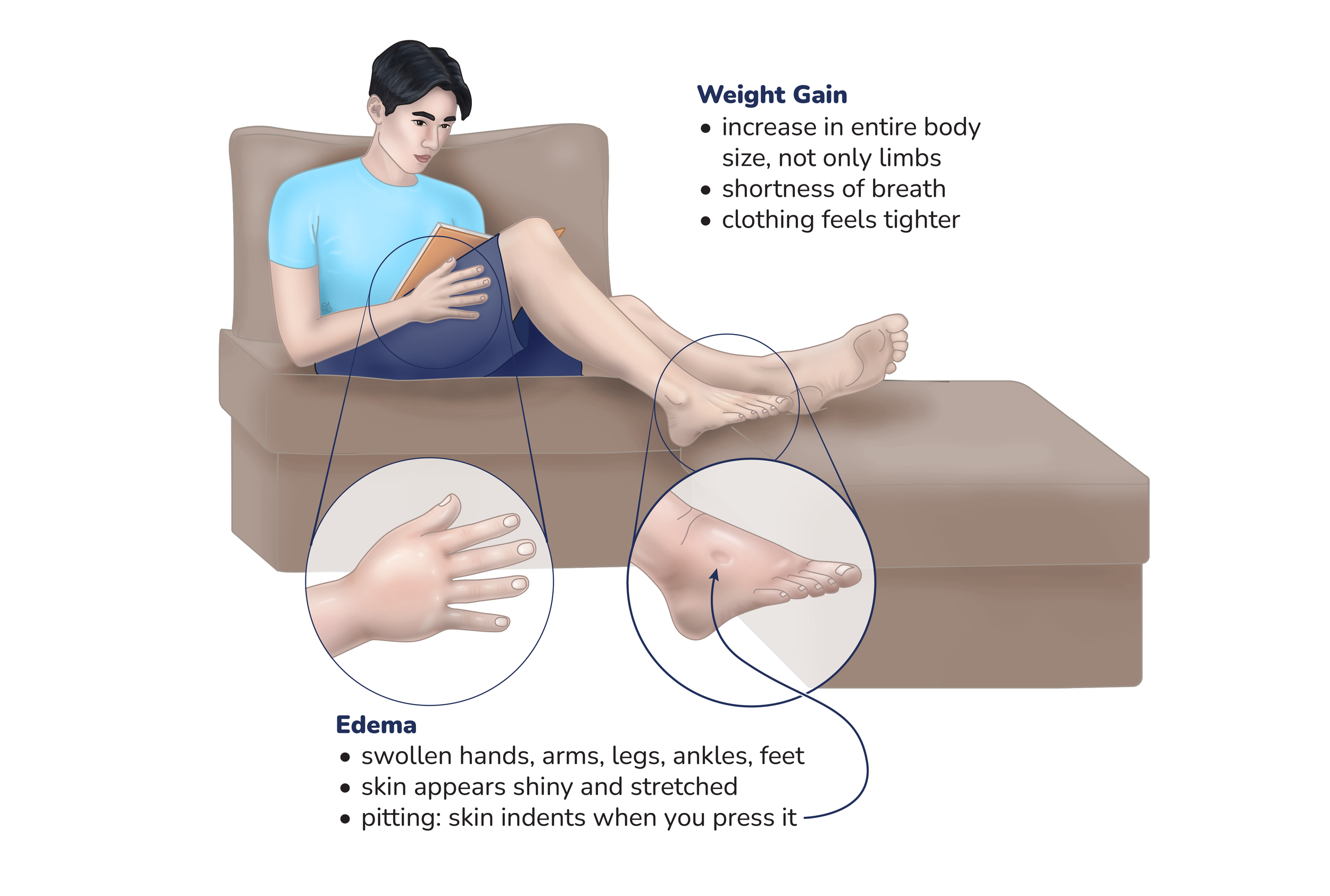
Edema & Weight Gain
weight gain caused by extra fluid in the body or an increase in body fat
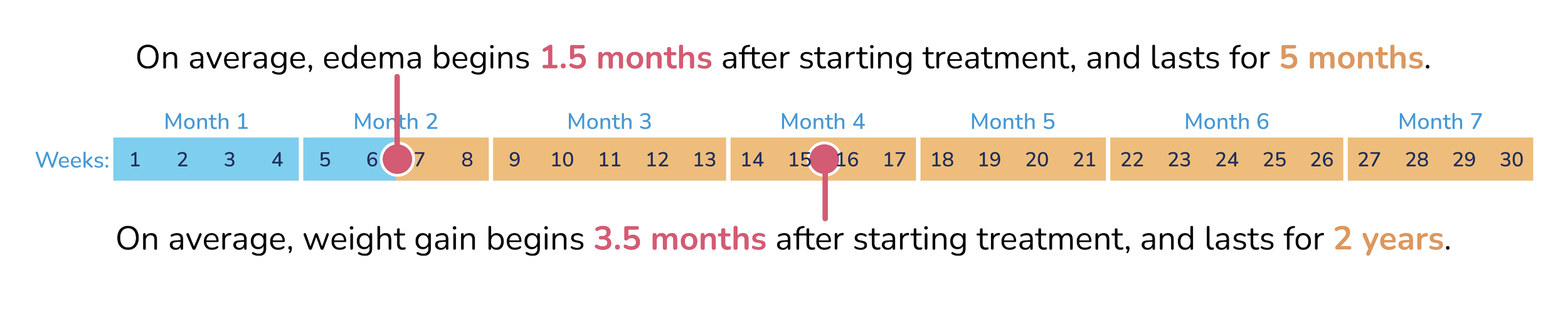
When do edema & weight gain start and how long do they last?
How serious is edema & weight gain?
How likely is it that I will experience edema & weight gain?
Prevention Strategies
-
Limit sodium intake and consider dietary counseling.
Aim to consume 1 tsp or less of salt per day.
Skip canned soup, deli meats, and frozen dinners.
Replace salt with alternative flavours such as herbs, garlic, or citrus.
Talk to your doctor about speaking to a nutritionist or a oncology-certified dietician.
Why: salt draws water into tissues and edema is caused by fluid trapped in body tissues.
-
Gentle exercise such as walking, swimming, and yoga can improve circulation and lymph flow to reduce edema and help maintain a healthy weight.
Seated calf raises and ankle pumps (pointing toes towards and then away from you) improve circulation.
Deep diaphragmatic breathing can help increase lymph flow:
Rest one of your hands below your ribs.
Take a slow, deep, breath in through your nose, feeling your hand rise as your stomach rises.
Slowly breathe out through your mouth, so your abdomen is flat again.
Repeat 5 times
Why: increasing circulation and lymph flow can prevent fluid from building up in your tissue, and exercise is a good strategy for preventing both edema and weight gain.
-
Weigh yourself at the same time each day (ideally in the morning).
Inform your doctor of weight gain of over 3 pounds in 24h or 5 pounds over a week.
Why: weighing yourself daily at the same time can indicate if you have fluid building up in your body because increased water retention adds weight.
Management Strategies
-
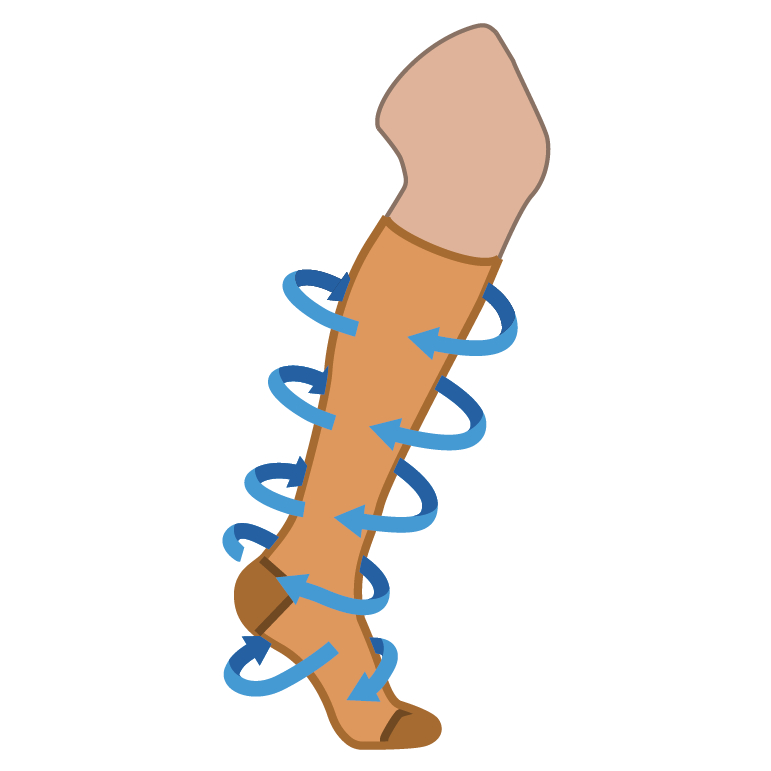
Compression garments:
Includes sleeves or stockings.
Compression garments apply various amounts of pressure:
15-20 mmHg ideal for mild cases.
20-30 mmHg ideal for moderate cases.
Wear them during the day and remove at night unless otherwise recommended by a healthcare professional.
Pressure should be firm and even but should not cause pain, numbness/tingling, or skin colour changes.
Why they might help: they put pressure on the area of swelling and encourage movement of lymph fluid.
Body positioning:
For arm edema: raise arm to a comfortable level with a cushion or pillow.
For leg edema: lie down while resting or if sitting elevate legs on a stool or chair.
For edema of the head or neck: sleep with 2-3 pillows to elevate your head
-
Dietary changes:
Discuss with your healthcare team about working with a nutritionist or an oncology-certified dietician.
Read food labels get a better idea of portion sizes and calories (low fat and non fat don’t always mean low calorie).
Exercise:
Discuss with your healthcare team about working with a physical therapist.
Build up physical activity with activities like walking, swimming, or yoga.
-
Before taking diuretic medications your healthcare team should evaluate blood pressure, kidney function, and electrolyte levels.
Diuretic medications can help get rid of fluid in the body by increasing urine production.
Two common medications are:
hydrochlorothiazide
furosemide
Emergent Symptoms
If you are unsure, it is always safer to seek medical care.
Tell emergency staff you are on an ALK inhibitor for lung cancer.
Call a Healthcare Provider
Call 811 for health advice from a registered nurse OR call your care team
Fast weight gain
New or worse swelling in legs, feet, hands, or belly
Mild trouble breathing when moving
Peeing less than usual
Swelling that feels tight or uncomfortable
You feel more tired and have swelling
Visit an Emergency Room
Call 911 or drive to your closest emergency room
Trouble breathing
Chest pain
Sudden swelling with pain or redness in one arm or leg
Swelling that quickly spreads up an arm or leg
Swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat
Fast weight gain with very little pee
No pee at all